A Rise in Glucocorticoid Levels Causes Which of the Following
12- The glucocorticoids A stimulate gluconeogenesis. A potent naturally occurring mineralocorticoid is.
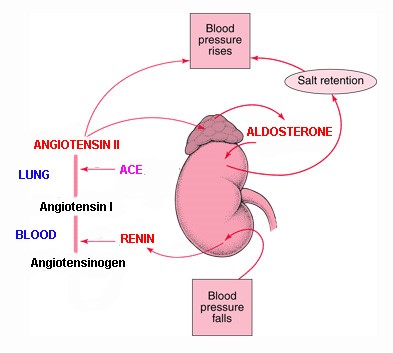
Aldosterone You And Your Hormones From The Society For Endocrinology
Glucocorticoid Gc excess from endogenous overproduction in disorders of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis or exogenous medical therapy is recognized to cause adverse metabolic side effects.

. A Hypoglycemia. B High cortisol levels will begin to cause ACTH levels to decline. Increased skin protein synthesis.
The glucocorticoid cortisol however promotes energy replenishment and efficient cardiovascular function. Increased activity of the glucocorticoid receptor in the muscles is associated with metabolic syndrome a group of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease stroke and diabetes. If blood glucose sugar levels remain high too often over time it has a damaging effect on many of the bodys organs primarily.
Animal studies indicate glucocorticoid-induced increased levels of serum lipids result in both increased formation of microemboli in the arteries supplying bone and fat-related blockage of venous flow from bone. CRH has been implicated as the initiator of circadian and stress-induced increases in glucocorticoid production and is subject to glucocorticoid feedback modulation. Excessive glucocorticoid levels resulting from administration as a drug or hyperadrenocorticism have effects on many systems.
Glucocorticoid excess due to pathology such as Cushings syndrome or prescribed synthetic glucocorticoids can cause immunosuppression muscle atrophy central adiposity hepatosteatosis osteoporosis insulin resistance hypertension depression and insomnia. It can also result in Cushings syndrome which can lead to. Enhances vasoconstriction to cause a rise in blood pressure and quickly distribute nutrients glucose to cells What can cortisol do to maintain blood pressure when put in stressful situations.
Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis GIO is a condition in which people who take medicines called glucocorticoids develop osteoporosis which means weakening of the bones. This glucocorticoid cascade hypothesis of stress and hippocampal damage was proposed to be involved in age-related accumulation of hippocampal damage in disorders like. The Gc receptor GR is widely expressed throughout the body including brain regions such as the hypothalamus.
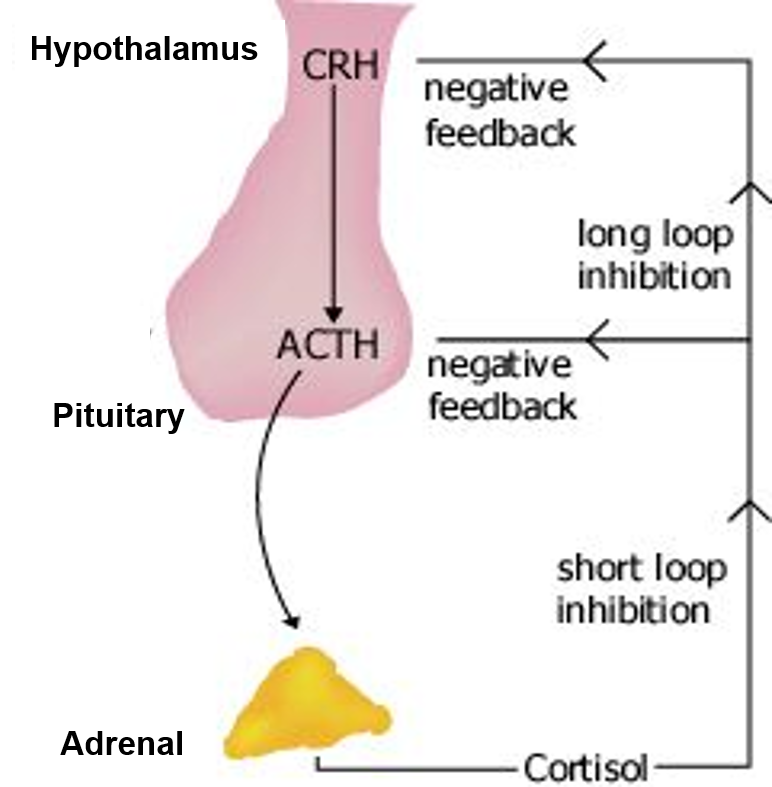
The change in ACTH levels in response to stress causes a decrease in glucocorticoid secretion from the adrenal cortex. D Aldosterone levels will increase. C High ACTH levels will begin to cause cortisol levels to decline.
Cortisol levels which vary naturally over a 24-hour period peak in the body in the early-morning hours just before waking. An increase in stress causes an increase in ACTH from the anterior pituitary. D Increased levels of ACTH.
A rise in glucocorticoids can promote insulin resistance. High blood glucose levels cause an increased secretion of A. Glucocorticoids also affect food intake during the sleep-wake cycle.
Glucocorticoid receptor signaling helps form fat cells in human tissues and can also cause abnormally high blood cholesterol or triglyceride levels dyslipidemia 13 1. Glucocorticoids suppress the immune system. Altered fat deposition and metabolism.
Some examples include inhibition of bone formation suppression of calcium absorption both of which can lead to osteoporosis delayed wound healing muscle weakness and increased risk of infection. Regarding the role of glucocorticoids in the aging process some studies show that an increase in glucocorticoid levels accelerates the aging process and increases the risk of premature mortality due to negative effects on vasculature adipose tissue and lipid and carbohydrate metabolism 102104. A proper response against stressors is critical for survival.
Long-term use of glucocorticoids can cause a loss of muscle tissue. The type you need depends on the specific health. Reduction in circulating lymphocytes.
- responds to the release of CRH by the hypothalamus A rise in glucocorticoid levels causes a decline in the production of ACTH and CRH. Activation of these pathways results in a quick physical response to the. The kidneys nephropathy the eyes retinopathy the nervous system neuropathy the heart heart attack the blood.
Modifications of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis and associated changes in circulating levels of glucocorticoids form a key component of the response of an organism to stressful challenges. - specifically targets cells producing hormones called glucocorticoid which effect glucose metabolism. C decrease glycogen synthesis.
Effects of the glucocorticoids include all of the following except. Osteoporosis increases the risk of breaking bones fractures even in low-impact situations for example a simple fall from standing height where otherwise a normal bone would not have. Due to an inhibitory control of the hippocampus on the HPA axis damage to this structure is expected to disinhibit the HPA axis causing increased glucocorticoid levels over time.
B increase the inflammatory response. Powerful anti inflammatory suppresses immune system inhibits healing alters mood increases appetite. The type you need depends on the specific health condition you have.
If both ACTH adrenocorticotropic hormone and cortisol levels increase which of the following would occur. In mammals the stress response is primarily mediated by secretion of glucocorticoids via the hypothalamic-pituitaryadrenocortical HPA axis and release of catecholamines through adrenergic neurotransmission. A ACTH production is increased even more by positive feedback.
A glucocorticoid is a kind of steroid. B increased CRH levels. There are no studies however on the direct effects of.
Inhibition of LT synthesis. Consistent with this role CRH mRNA in the PVN of Sim1Cre-GRe3Δ mice in which we find high glucocorticoid levels is 3 times higher than levels in control and Sim1Cre-GRe2Δ mice. Increased levels of glucocorticoids promote gluconeogenesis mobilization of amino acids and stimulation of fat breakdown to maintain circulating levels of glucose necessary to.
C increased levels of cortisol. D stimulate glycogenolysis 13- Which of the following will decrease glucocorticoid secretion by the adrenal cortex.

Female Reproduction Iv Parturition And L Actation Parturition And Lactation The Factors That Stimulate Parturiti Endocrine System Uterine Cervix Lactation

Cortisol An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Dhea For Women How To Heal Hormonal Imbalances Caused By Adrenal Fatigue Dhea Hormone Imbalance Female Hormone Imbalance

Definition And Facts Of Adrenal Insufficiency Addison S Disease Niddk

Adrenal Insufficiency Pathology Review Osmosis

Cortisol An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Adrenal Insufficiency Endotext Ncbi Bookshelf

Addisons Disease Disease Quote Addisons Disease Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Symptoms

Week 7 Endocrine System Flashcards Quizlet

Cortisol Function Tests And Effects Of High Low Levels

Understanding Cortisol Cortisol Matters

Oxytocin Biosynthesis Oxytocin Is Synthesized In The Cell Bodies Of The Magnocellular Neurones Of The Paraventricu Oxytocin Endocrine System Sensory Nerves

Pediagenosis Endocrine System Chronic Kidney Disease Hypoparathyroidism

Cortisol An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
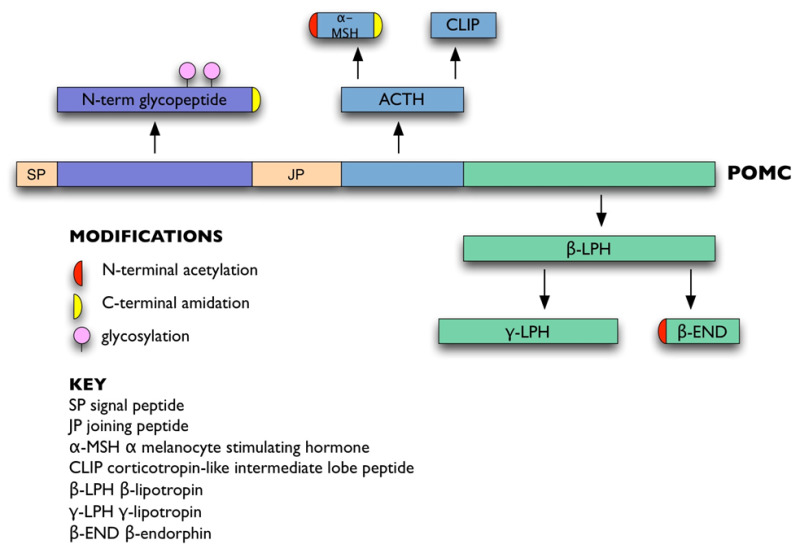
Normal Physiology Of Acth And Gh Release In The Hypothalamus And Anterior Pituitary In Man Endotext Ncbi Bookshelf

Adrenocortical Tumours Tumor Adrenal Disease Hirsutism
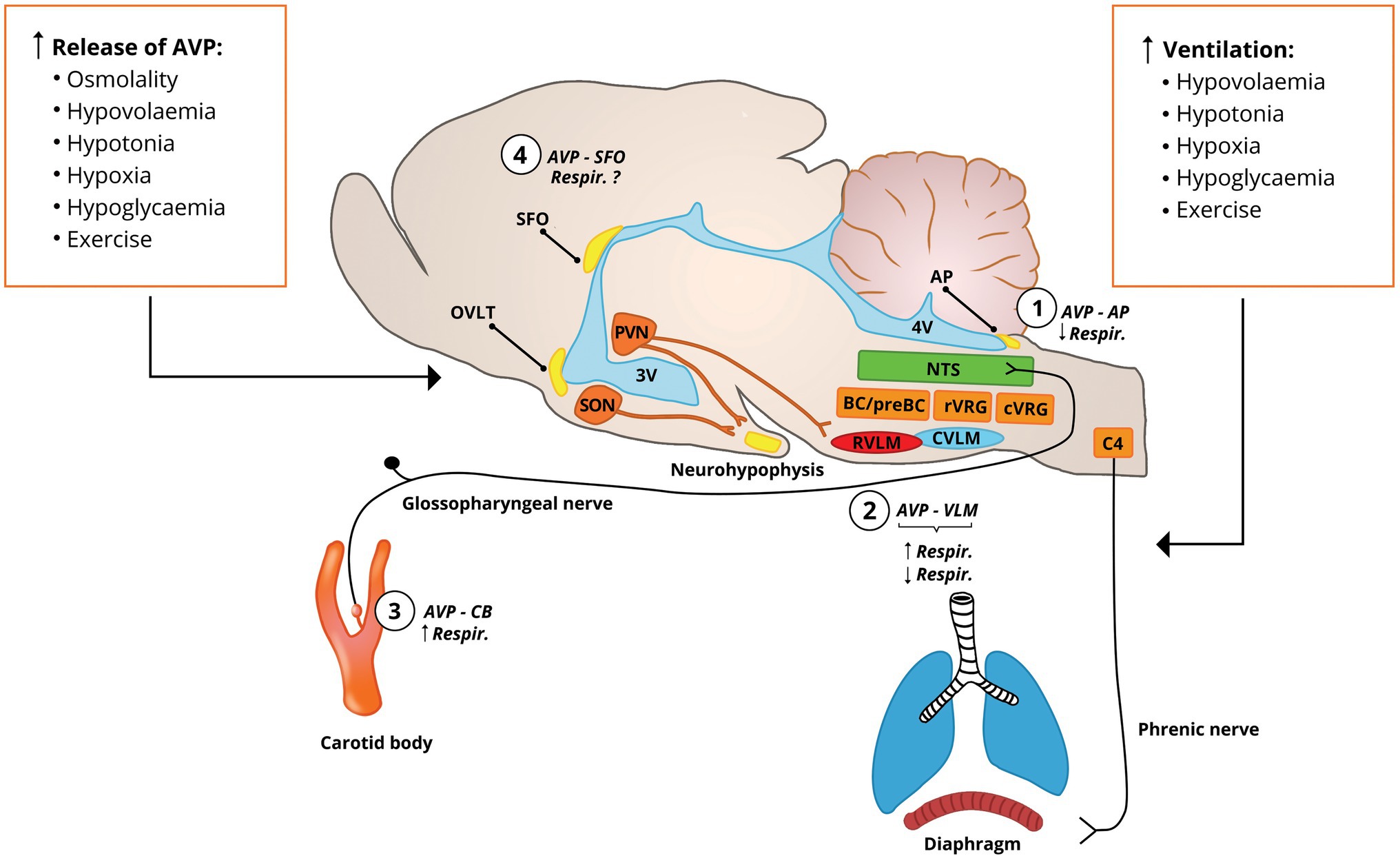
Frontiers Vasopressin And Breathing Review Of Evidence For Respiratory Effects Of The Antidiuretic Hormone Physiology
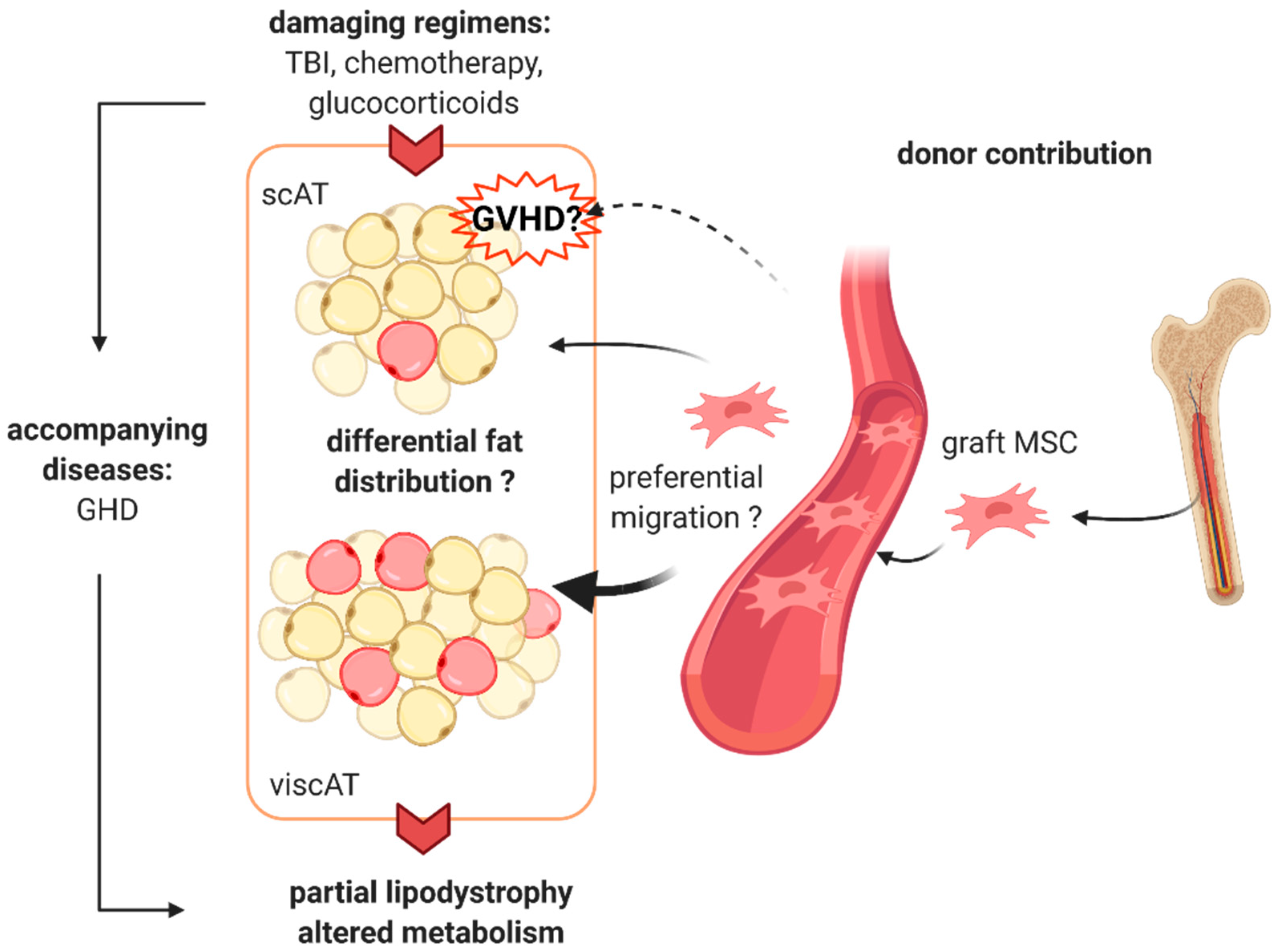
Jcm Free Full Text Lipodystrophy As A Late Effect After Stem Cell Transplantation Html
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone You And Your Hormones From The Society For Endocrinology
Comments
Post a Comment